
Warmest thoughts and best wishes for a cheer filled season and a very happy and healthy New Year!
May your days be merry and bright.
Merry Christmas!

Warmest thoughts and best wishes for a cheer filled season and a very happy and healthy New Year!
May your days be merry and bright.
Merry Christmas!

Ten US states brought a lawsuit against Google, accusing the search giant of “anti-competitive conduct” in the online advertising industry, including a deal to manipulate sales with rival Facebook.
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton announced the suit, which was filed in a federal court in Texas, saying Google is using its “monopolistic power” to control pricing of online advertisements, fixing the market in its favour and eliminating competition.
Google, which is based in Mountain View, California, called Paxton’s claims “meritless” and said the price of online advertising has fallen over the last decade.
Paxton led a bipartisan coalition of 50 U.S. states and territories that announced in September 2019 they were investigating Google’s business practices, citing “potential monopolistic behaviour.”
Now Texas is bringing the suit along with other Republican attorneys general from Arkansas, Idaho, Indiana, Kentucky, Mississippi, Missouri, North Dakota, South Dakota and Utah.
The complaint targets the heart of Google’s business — the digital ads that generate nearly all of its revenue, as well as all the money that its corporate parent, Alphabet Inc., depends upon to help finance a range of far-flung technology projects.
As more marketers have increased their spending online, those digital ads have turned Google into a moneymaking machine. Through the first nine months of this year, Google’s ad sales totalled nearly $101 billion (€82.5 billion), accounting for 86% of its total revenue.
And now the states contend Google intends to use its alleged stranglehold on digital ads to choke off other avenues of potential competition and innovation. The company struck an illegal deal with Facebook, a major competitor for ads, to manipulate advertising auction, according to the complaint. Facebook declined to comment.
In the “ad tech” marketplace that brings together Google and a huge universe of online advertisers and publishers, the company controls access to the advertisers that put ads on its dominant search platform. Google also runs the auction process for advertisers to get ads onto a publisher’s site. Nine of Google’s products in search, video, mobile, email, mapping and other areas are estimated to have over a billion users each, providing the company with a trove of users’ data that it can deploy in the advertising process.
Google officials say the company shares the majority of its “ad tech” revenue with publishers, such as newspaper websites. An official recently rejected even the assertion that Google is dominant, saying that market dominance suggests abuse, which is foreign to the company.
The state’s suit comes after the U.S. Justice Department sued Google in October for abusing its dominance in online search and advertising — the government’s most significant attempt to buttress competition since its historic case against Microsoft two decades ago.
Separately, the FBI is investigating whether Paxton, a close ally of President Donald Trump, broke the law in using his office to help a wealthy donor who is also under federal investigation. This fall, eight of the attorney general’s top deputies accused him of bribery, abuse of office and other crimes in the service of an Austin real estate developer who employs a woman with whom Paxton is said to have had an extramarital affair.
All eight of Paxton’s accusers have since been fired or resigned, including the deputy attorney general who had been leading the office’s probe of Google. The court complaint list attorneys with private firms in Houston, Chicago and Washington, D.C., as the lead lawyers on the case.
Paxton announced the lawsuit the week after the U.S. Supreme Court rejected his legal push to overturn Joe Biden’s victory in the presidential election, a case that prompted widespread speculation that the attorney general is angling for a preemptive pardon from Trump.
The American Economic Liberties Project, an organisation that advocates for government action against business concentration, welcomed the states’ suit.

The E-Commerce Times reports that in the midst of the pandemic mobile shopping apps have become central to online retail operations and they’re clearly here to stay.
In fact, by 2021 mobile e-commerce, or m-commerce, sales are expected to account for 54 percent of all retail ecommerce sales.
The reporters spoke with m-commerce specialists to find out what’s behind the rapid growth of consumers shopping on mobile devices, what mobile shoppers require from shopping apps, and how retailers can provide a better experience for their customers who use mobile devices.
Steven Boal, CEO of Quotient argues that shopping apps are popular with consumers because they are a great way to experience a brand in an immersive digital setting. By this, he means that shopping apps can have the same experiential effect as a physical store where consumers can experience a shopping environment that’s created for physical discovery but conveniently anytime and anywhere.
Consumers can the same way take part in loyalty programs, order and have things delivered.
Besides, 81 per cent of Americans have smartphones and use them a lot every day. Companies try hard to make their apps simple to use.
Heidi Bullock, CMO at Tealium agrees saying that convenience is increasingly driving the consumer experience. Beyond just being convenient, shopping from smartphones or tablets also allows consumers to shop in-the-moment and solve the problem on the spot. A centralized hub for consumers’ relationship with a brand makes shopping personalized.
Rob Fagnani, head of business development and operations at Formation, points out that shopping apps should be easy to navigate to discover and find the right products, have seamless payment and commerce flows, and more than anything, tailor the experience as much as possible to the user, everything from the product assortment to individualized offers.
To feel useable and relevant, apps must also ultimately fit naturally into the daily life of consumers.
People want to download an app and instantly understand how it works, whether they’re looking for a particular item, browsing a weekly sales ad, or scrolling through the latest promotions. When those promotions are tied to the consumers’ behavior or previous interactions, you can create a warm, unique, memorable and valuable experience.
Evolving the experience over time so that it is personalized and anticipates the user’s next need is a key component to mobile app success,” Britt Mills, senior director of customer experience for Mobiquity, told the E-Commerce Times.
Experts forecast that shopping apps will continue to evolve with consumer demand and needs but as some customers are comfortable going to physical shops now, many brands need to continue maintaining and growing their physical and digital storefronts for the months and years to come.
Consumers are likely to continue using a blend of in-store and digital solutions even when the world returns to normal. Retailers should explore ways to make their digital solutions blend with in-store.
It will not be enough to just advertise your products, but you will have to actively pursue and engage your potential customers, through avenues such as tailored remarketing, custom UX for every client on each app, and seamless checkouts.
You can see the beginning of this already taking place with the integration of social media and marketplaces, such as Facebook and Instagram, and with the likes of TikTok and YouTube following suit. A seamlessly-tailored online experience between social and business is the next step in a world tailored to each individual.

Ecommerce News Europe writes that ecommerce fraud is becoming a real problem in Germany.
The reason is the preferred payment method of German shoppers.
A common form of ecommerce fraud is when the scammer orders something online, chooses to pay on account, provides a false or found name and account number, and gives a certain address where he can then pick up his order. The fraudster runs off with his expensive, but free product, while an innocent person is stuck with the bill.
Only getting someone’s name and date of birth can sometimes be enough to trick online shops.
A television crew spoke with the head of a gang of about 200 fraudsters. He’s currently in prison as he got arrested after six years of investigation. He and his network stole about 13 million euros, generated through about 26,000 online orders.
According to the Russian fraudster, he deliberately chose Germany after trying to commit fraud in several other countries. “Compared to other countries, the security system in Germany is the weakest”, he says.
The fraudster blames the companies that make their payment mechanisms available to online retailers in Germany.
German online shoppers like to buy on account as it is easy. Most retailers have little choice but to offer the risky invoice as a payment method. A spokeswoman for service provider Ratepay admits that if they make paying too difficult, nobody buys anymore and then they don’t make any more sales.
There are always additional security measures like two-factor authentication. But most consumers see these things as a hurdle as well. For the online retailer, it’s weighing security against sales.
Consumers are also hurt by the crime. For example, in a woman’s name there were goods ordered with a total worth of 6,000 euros, leading to trouble with debt collection agencies and possible Schufa entries (credit record in Germany).
And there is a simple, but painful reason she didn’t notice anything about the supposed orders until the reminders came. For many online shops, it’s sufficient to get a real name and date of birth in order to offer purchase on account. A customer would also have to provide a home address and e-mail address, but these won’t get checked. They can therefore be set up by the fraudsters themselves.
According to Stefan Keller from the law enforcement agency in Berlin, there were over 19,000 cases in the city-state alone last year. And the clearance rate is only 12 percent.
KPMG has introduced a blockchain-based solution for keeping a record of CO2 emissions
KPMG, an audit company, has announced the development of the Climate Accounting Infrastructure (CAI) blockchain solution that allows you to keep records and track greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. Blockchain in combination with IoT will ensure the company’s environmental data security, which will help to assess climate risks.
Climate data is gaining significant financial weight and, as a result, corporate financial risks depend on the transparency and non-falsifiability of this data. Blockchain in the field of climate and ecology can reduce risks and increase the predictability of financial flows.
Eight banks have launched a trade finance platform based on the Contour blockchain
Obtaining financing is one of the key processes in the work of companies, while traditionally obtaining trade finance requires a lot of time and complex approval procedures, which creates operational difficulties for companies and leads to additional costs. The acceleration of obtaining trade finance through blockchain can reduce costs for large companies and reduce the risks and operational problems for small and medium-sized businesses, which often have cash gaps.
The Contour blockchain-based trade finance platform has been launched on the R3 Corda blockchain. It is designed to optimize and speed up traditional trade finance processes by digitizing them. The platform now faces the task of optimizing the process of issuing letters of credit between the parties. Issuing a letter of credit using traditional methods takes an average of 10 days. Contour processes the letter of credit per day — the time is reduced by 90%.
SKODA, Lumos Labs and Microsoft India have launched a blockchain development program
SKODA AUTO DigiLab India and Lumos Labs have announced the creation of the Microsoft Century Program, an enterprise blockchain startup program. The companies plan to use their own development experience and expertise in the field of digitalization to help blockchain startups solve business problems. The acceleration program is designed for 18 months.
Honda and General Motors create a decentralized car charging network
Electricity transmission is one of the largest resource markets, but there are significant losses caused by inefficient distribution and consumption of electricity. The tendency to decentralized energy networks is spreading around the globe. Energy networks are formed not only by traditional suppliers, but also by small players who produce “ecological” energy on their own sites.
Blockchain is good to coordinate this increasingly complex network and manage payment and consumption transactions in a timely manner. The issue becomes even more relevant in the times of switching to electric vehicles.
The Mobilitu Open Blockchain Initiative (MOBI) consortium, which includes major automakers has developed a standard for integrating blockchain into a decentralized electric vehicle charging network.
The project specifications are not tied to a specific blockchain and aim to lay the foundation for decentralized charging networks and allow them to efficiently use excess moving energy. These solutions allow you to securely identify yourself on the network, interact using a standard message format and automatic entries in the transaction register, such as charging, generation and data exchange between electric vehicles, charging stations and power settings.
Residents of the French city used a blockchain app to vote on road construction
Voting is another promising area for block-chain implementation. For example, residents of the small French town of Verneuil-sur-Seine, 30 km from Paris, used the Avosvotes app on the Tezos blockchain to vote on new roads. The app will provide security, transparency of voting and help solve the problem of low turnout.
In the US, digital signatures on the blockchain can gain legal significance
The bill on this was submitted to the relevant Committee on energy and trade, amendments are being made to the Electronic signatures in global and national trade act.
If approved, the requirements of the law will apply to electronic signatures and smart contracts on the blockchain, which will significantly push the spread of blockchain for signing contracts, as well as fully legalize the use of smart contracts in the business sphere, and in general will be a big step for the blockchain in the global economy. Currently, signing contracts on the blockchain is legalized only in a few US States.
Cambridge University study: 43% of all existing blockchain solutions are made by financial companies
According to a survey of 200 organizations (companies, startups, banks, government agencies) in 59 countries in 2018-2019, in 43% of all industrial use of blockchain these solutions are used in the financial sector. At the same time, the development lifecycle of a blockchain project turned out to be quite long: on average, it takes about two years from the concept stage to deployment, and larger networks may require up to four years. 48% of the projects included in the sample were created on Hyperledger, 15% on the basis of R3 Corda. 22% of blockchains were developed within consortia, 70% by companies alone, and 5% by state organizations.
BMW’s South Korean division will launch a blockchain-based loyalty program
The use of blockchain to distribute bonus points for loyalty programs is a fairly small but important case for testing blockchain technology and its advantages in a multi — billion-dollar car market with millions of customers. BMW has previously reported developments in using blockchain to track vehicle information.
BMW Korea has announced the launch of the BMW Vantage blockchain solution for the loyalty program. BMW Vantage will allow customers to accumulate bonuses that can be used to purchase goods and services, for example, to pass a technical inspection with a discount. Users with a certain status in the program will be able to attend private events of the company. Points will be awarded through the app for purchases of both new and used cars. The first users of BMW Vantage will be residents of South Korea, but the company plans to expand the program to other countries.

Business Insider and eMarketer analysts estimate that the volume of global e-trade will amount to $3.914 trillion in 2020. See the main results of their report below.
Online sales in Western Europe, with an overall decline in retail turnover by 9.9%, will grow by 16.9% reaching $498.32 billion by the end of the year. The earlier predicted figure is 8.8%, which is $10.83 billion less than the current forecast.
“We previously expected retail sales in eCommerce to account for 11.0% of total retail by the end of the year, but we revised this figure to 13.2%,” the report says.
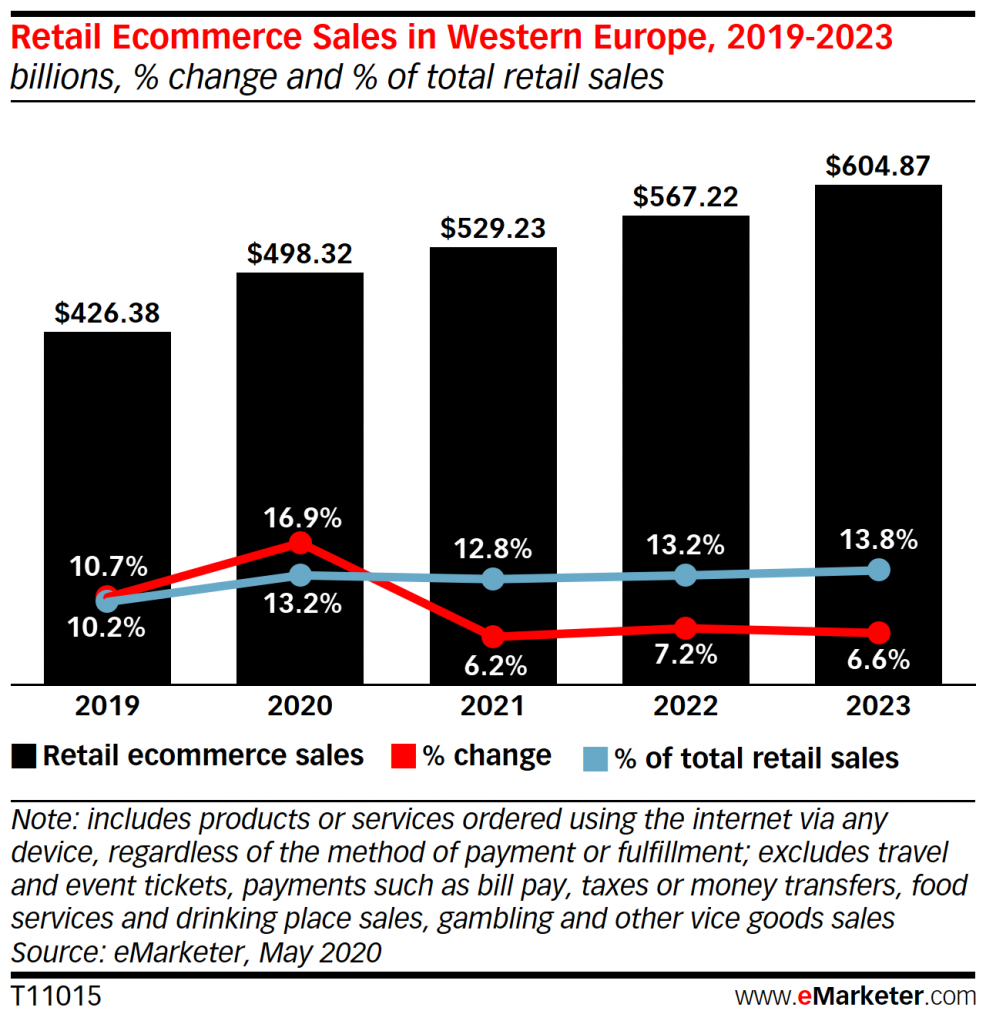
A number of European countries will grow significantly above the general market. Thus, online stores in Spain will increase their sales by 22.9%, the highest rate in Western Europe and one of the fastest in the world. The market of the Netherlands will grow by 21.9%, and Italy – by 20.5%.
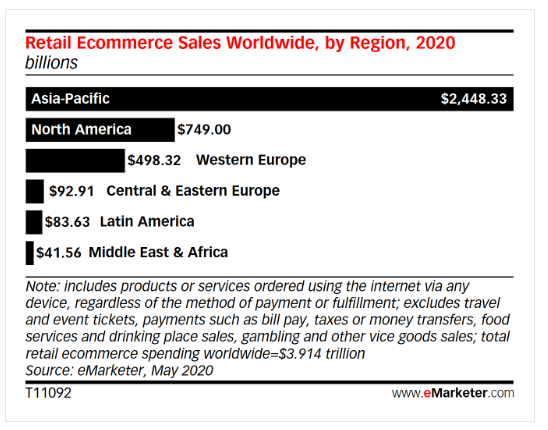
Due to China’s overwhelming dominance in the global e-commerce market, the Asia-Pacific region holds a 62.6% share of the total market. North America and Western Europe will have shares of 19.1% and 12.7% respectively by the end of the year.
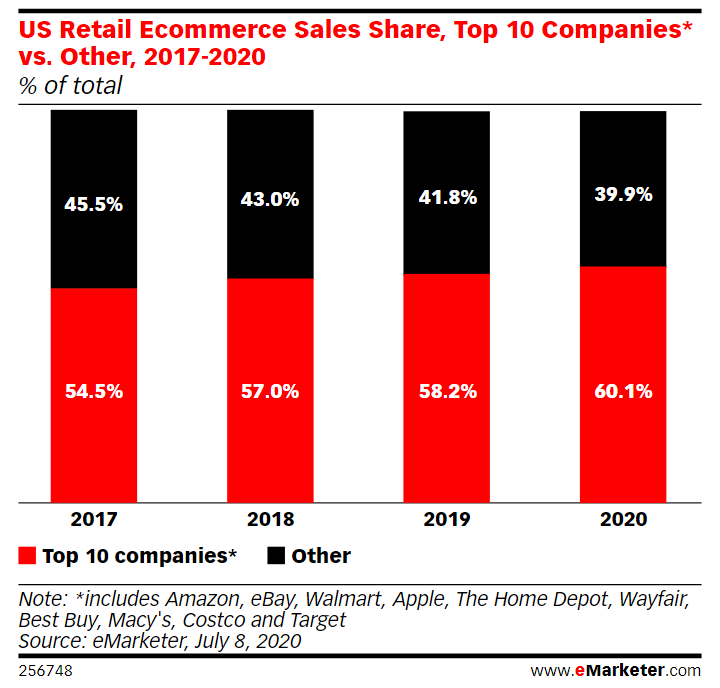
In the United States, the top ten online retailers will account for 60.1% of total e-commerce turnover in 2020, up from 58.2% last year. Top 5 sellers: Amazon, eBay, Walmart, Apple, the Home Depot. In the past few months, consumers have increasingly turned online to networks such as Target and Costco. During the pandemic, each of these companies experienced a surge in online sales.
“We expect that the top 10 retail companies engaged in e-commerce will increase the volume of online sales at a faster pace. They will increase by 21.8%,” the authors of the report believe.
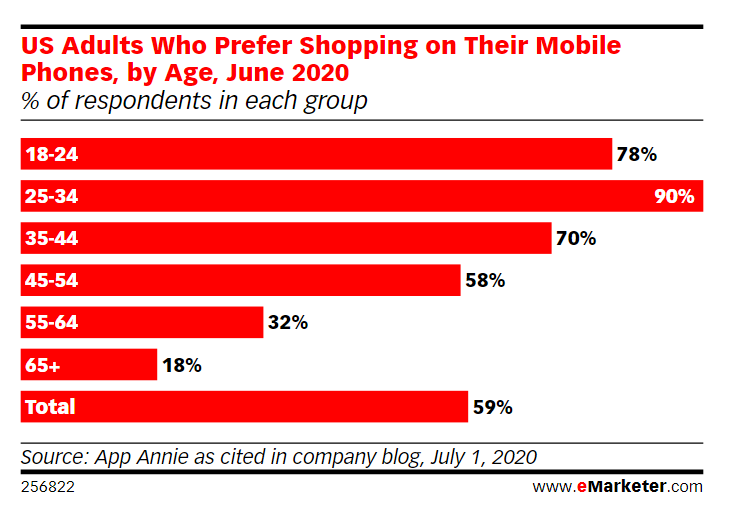
Mobile commerce has shown a solid growth recently: in the UK, it accounts for about half of all online orders. The most active of the European countries is growing m-commerce in Germany. In the US, the pandemic has shown that young people also prefer smartphones to computers.
This year the number of “mobile buyers” in the US (those who used their mobile device to make at least one purchase through a mobile site or application) will reach 167.8 million. By 2024 this figure will grow to 187.5 million people, or two-thirds of the population of the USA.
In the 18-24 age group, this is 75% of users, and in the 25-34 group – all 90%. But even here, China will overtake other countries: the average time that Chinese people spend daily on their smartphones will grow this year to 2 hours 43 minutes, which is 17.9% more than a year earlier.
*our special thanks to www.e-pepper.ru

The pandemic clearly showed that in fact, the only alternative to closing a business was online sales. Even if a company’s website was in its infancy, it was urgently setting up standard tools for e-commerce: lead generation, traffic generation, and sales. The key problem that remained was attracting the attention of potential customers to their resource. It was even more difficult as people started to buy less because of falling real incomes and under stress from viral threats and long self-isolation.
Customers who once refused to buy a product of a certain brand return with great difficulty. The company, which lost the ability to remind customers of itself in the usual channel during isolation, had to use online loyalty tools to return sales.
Thus, in these difficult circumstances, when customer interest is at a very low level, marketers need not only to bring a potential buyer to the retailer’s site, but also to show them exactly those products that they are most likely to like, otherwise the purchase will not take place.
Data researchers and data scientists help you find out your customers ‘ preferences. Using predictive analytics tools, they identify people with common behavior patterns among all their clients, form clusters, and then use it to prepare the most personalized offer for each cluster.
Clusterization is not about segmenting customers on formal grounds like by age, gender, place of residence. Clusterization helps you identify truly homogeneous groups with similar attitudes to purchases and the same problems, preferences, interests, or lifestyle. This mathematical procedure is based on a statistical approach and allows you to programmatically identify the most significant parameters of consumer behavior of buyers. Then, again, using software methods, you can create trade offers for many identified small groups and promote them through different channels.
For instance, a customer is looking for the products they need on your website and popular items from the related category are automatically pulled up.
Connecting recommendation services to online store sites gives good results.
When the data analyst has formed clusters of buyers, it is necessary to predict which product is likely to be offered to which clusters of buyers. Knowing the preferences of customers in a particular cluster, the specialist builds a table for the probability of purchasing a specific product.
For a company with a customer base of about 12 million people and about 200 thousand products in the active range, such a table can consist of more than 240 billion cells: horizontally-people, vertically-products. This amount of data will break Excel down, but machine learning can handle this task.
The table can be filtered by the highest probability of purchase (we are interested in at least 50%), then we will see everyone who is sure to buy these products. At the same time, you will be able to find out which of the buyers does not buy anything and creates an outflow. Using the table, we try to offer this segment of customers several types of goods and see how customers react.
It is possible to predict the purchase of goods not only here and now, but also for a long time.
Predictive analytics is still a new marketing tool, and retail, of course, is very heterogeneous, so the wariness of many companies is clear: will machine learning be effective in a particular segment of the industry? In this case, you should first conduct a pilot project and based on its results, make a decision to launch the service into productive operation. You should start using machine learning technologies by embedding models in existing processes and systems (for example, CRM) to get the fastest possible return.
However, at the beginning of online development, it is too early to engage in data analytics, since the company does not have stable traffic yet and, in fact, there is nothing to analyze. Any work of this kind begins when a good amount of data already collected.
Major retailers’ IT departments understand that it is easier to give the task to an experienced third-party contractor than to look for specialists inside, especially if the company has never had such a project. You need to look for companies that consist of industry experts and a data science team. Projects can be called effective when their results are transmitted with the source code, open source technologies are used, and the customer company forms its own competence center based on the results of the project.
If the company is ready to finance the development of its own e-commerce team, this will be the best investment. After the project it will keep its own specialists and raise funds through predictive analytics. Client traffic generation will continue. With constant work in this direction, the model, which is continuously in the process of self-learning, will learn data better and make predictions more accurately.
If you can’t afford to hire data scientists, you can optimally use predictive analytics based on cloud services or SaaS (Software as a Service) solutions.

Covid-19 has changed economic and social life making our dependence on digital technologies even stronger. Of course the trend has had a great impact on the banking sphere which started experimenting with digital technologies even before the virus appeared. Even before Covid-19 retail banking started changing: branch usage was declining while customers preferred using digital channels to manage their money. Adopting digital technologies is quick in the US and the EU countries like Italy and Spain. In other markets the trend is also visible but goes slower. According to McKinsey report dated July 30, 2020 top performers in the banking sphere made a shift to digital technologies before the pandemic and greatly outperformed their competitors in terms of distribution channels.
In terms of digital services the research has shown great customer satisfaction (60-85%) with banking from home in the EU and the US. Even elderly clients got used to transactions via mobile apps. Biometric authentication, quick balance checks, and easy transfers are increasingly table stakes for banking apps. However, leaders take a customer-centric mindset to developing new features that will make users even more attached to digital technologies. Personalized home pages in the apps are already widely used and hailed by clients.
While in many markets the crisis caused a significant drop in monthly unit sales across all channels, it also accelerated the sales mix redistribution as channels recovered at varying speeds. This has made digital sales penetration jump especially with leading banks. Leading banks doubled their digital cross-sell rates (digital sales per digital user) between 2015 and 2019 to 4.2 times that of slow adopters. To achieve this result they regularly tested and launched new capabilities, used customer-relationship-management (CRM) tools to create preapproved offers, streamlined journeys with prefilled applications, and used digital signatures for instant fulfillment. A lot of customer-behavior analysis has also contributed to sales increase.
Research has shown that before Covid-19 outbreak inbound calls to contact centers started giving way to other communication channels. But the first days of self-isolation were characterized by a steep rise of such calls since uncertainty requires contact. At the same time in markets with developed digital communication channels this rise wasn’t that steep. As a result, the pandemic has brightly illustrated demand for digital communication in banking. Practice demonstrates that interactive voice response (IVR) is helpful but modern banks are turning to next-generation tools, data, and analytics to optimize the end-to-end call funnel. Chatbots are used to retain customers in digital, reducing inbound calls. IVRs are evolving to be conversational and enhanced with contextual awareness that leverages historical interaction data to provide personalized query resolution and protect agent capacity. In the research by McKinsey it is mentioned that many banks have also experimented with remote advisory models, such as branch-to-branch, branch-to-hub, or hub-to-home. These capabilities are said to offer convenient access to complex advice and match customers to the right specialists, making conversations more efficient.
The virus and the social distancing caused by it triggered the closure of many branch offices even among leading banks. After the gradual revival from self-isolation the trend remained viable. Some banks boldly cut down the number of branches while others acted in favor of gradual changes. Yet, McKinsey research demonstrates that the bold bankers happen to be more efficient and successful. The reduction was quick but it was also about operational restructuring. To shift the operating model, leaders began to reskill profiles toward universal banker roles to better respond to the lower volume but wider variety of demand coming into branches. Branch formats were changed to create formats tailored to customer needs in specific areas. These ranged from large flagship branches to mini branches with a high degree of self-service, remote advice capabilities, and flexible opening time in low-traffic areas.
Thus, the pandemic has accelerated the process of the banking sector digitalization. The digitalization itself is beneficial for banks as it leads to cost-cutting and to clients who become more satisfied with managing finances from home and using customized digital banking products.
To learn more you can consult the full report: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/breaking-away-from-the-pack-in-the-next-normal-of-retail-banking-distribution#
Artificial intelligence will play a central role in the economy of the future and serve as a growth driver. Application of artificial intelligence ranges from predictive analytics and chatbots to fraud prevention and regulatory compliance. Banks ‘ investments in machine learning technologies grow by an average of 46.2% annually, but many projects remain incomplete. So the question is how to make such projects effective.
Two effective approaches to implementing AI in banking
For the past three years the banking industry has been gripped by a real “gold rush” in terms of artificial intelligence. Banks have created a lot of data lakes, launched a lot of AI initiatives, and spared no expense in attracting the best young specialists in data processing and analysis.
And what do we see as a result of these 3 years? There was a lot of sand and very, very little gold. According to Gartner, 80% of AI projects have failed or have not progressed beyond prototype development.
What is the reason for this? It seems that all the necessary prerequisites were available for the success of the projects:
Evaluating the results, one can assume that banks are very actively engaged in business, without having thought through a strategy for working with data. In many large projects that have been launched, responsibility has been assigned to its departments, rather than to business units.
For the AI projects to bring results, it makes sense to follow two strategic approaches.
The first is that machine learning capabilities are adapted, implemented and integrated into all banking applications for the front office and back office, including for digital interactions with customers, compliance with regulations, financial management and HR management. As a result, customers can use AI capabilities directly at the time of the transaction.
The second approach is to focus on specific cases with a clear understanding of business goals. Being specific is helpful for performance assessment and result orientation.
Indeed, rushing for AI projects banks faced many difficulties and here come recommendations for making such projects effective:
How banks can develop an effective AI strategy
Many banks initially treated data lakes as a sacred cow when working with AI. However, some of these data lakes have unfortunately turned into swamps. As a result, data processing and analysis specialists and developers began to move to financial technology companies where there were no problems with data and getting access to it, unlike in banks.
Gartner analysts estimate that 70% of the AI effort is spent on data management: getting, cleaning, preparing, and processing.
To ensure that customers do not have to spend time moving data, updating it, and ensuring its integrity, it makes sense to implement machine learning algorithms, such as R and Python, directly in the data source in real time.
At the same time, it is possible to implement innovative tools for autonomous data management to reduce the load and significantly simplify all standard AI operations. This radically changes the paradigm of working with AI data, as users can fully focus on their strategic analysis.
Thus, banks will be able to extract the gold that is hidden in various internal data sources faster and with much less effort.
Artificial intelligence under control
AI conclusions reliability is of increasing concern to regulatory authorities in many countries, that is why they are increasing their supervision of banks ‘ initiatives in this area. Banks have to explain the logic of machine learning models to them. In particular, this applies to the use of AI in robots-investment consultants, for recommendations on transactions or monitoring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Regulatory authorities also have requirements for data localization. To meet these requirements, it is possible to create a virtual machine learning platform in the private cloud inside the data center, protected by firewalls. If data sets do not contain personal data, sometimes they can be processed in a hybrid environment or a public cloud.
Thus, continuous cooperation between banks, regulatory authorities, and technology partners is very important for transparency, reliability, and compliance with ethical values when banks work with AI.

Banks’ applications and applications of other similar organizations may stop working on smartphones manufactured by Huawei and Honor. The new restrictions on the Chinese company are reported by the Washington Post.
On August 13, Huawei’s temporary general license (TGL) expired. The license allowed the US companies to cooperate with Huawei, which is currently under sanctions. According to experts, due to the license loss, Google will stop producing security updates for Huawei smartphones and its subsidiary brand Honor. This applies to both new and old devices released before the Chinese corporation was included in the US sanctions list in May 2019.
It is reported that Huawei devices will no longer receive the SafetyNet certificate from Google. In this case, apps that require this certificate will stop working on smartphones. Experts explain that the manufacturer’s devices may be left without banking and payment applications, as well as some programs with built-in microtransactions.
Representatives of the US Commerce Department explain that the temporary delay is necessary in order for the US communication providers and other companies to find new suppliers instead of Huawei. It remains unknown whether the TGL will be extended. In a comment to the Washington Post Huawei claims that it is assessing the potential consequences of the license expiration and is monitoring the situation.
On August 15, the Trump Administration granted the Pentagon a temporary waiver from a nationwide ban on contractors using Huawei products. The temporary suspension is valid from August 13 to September 30. During this time, defense contractors must find suppliers to substitute for the Chinese equipment.